The Concept of Feasible Scenario Spaces (FSS)
Feasible Scenario Spaces (FSS) is an essential concept for strategic planning and decision-making, particularly in complex environments characterized by numerous parameters and uncertainties. FSS refers to the range of scenario parameters within which a particular capability set can achieve success while maintaining acceptable levels of risk. This structured approach helps leaders assess the viability and desirability of various strategic options, prioritize resource allocation, and develop contingency plans to mitigate risks.
Key Components and Considerations
Feasible Scenario Spaces (FSS) is a basic strategic framework used to explore and evaluate the range of possible futures in complex and uncertain environments. By identifying and analyzing key parameters, capabilities, and success criteria, the model helps entities delineate the scenarios within which they can achieve their goals while maintaining acceptable levels of risk. It simply provides a structured way to anticipate challenges, prioritize resource allocation, and develop contingency plans, allowing decision-makers to navigate uncertainty with greater confidence. In the context of the AI race between China and the United States, applying FSS enables a way to systematically examine the competitive landscape and envision the potential trajectories over the next decade.
1. Scenario Parameters
Scenario parameters define the environment or situation under consideration. These variables include market conditions, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and competitor actions. Identifying and understanding these parameters is crucial for defining the scope of the analysis.
2. Capability Set
The capability set encompasses the resources, assets, skills, and strategies available to an organization. This includes tangible resources like technology, infrastructure, and financial capital, as well as intangible assets such as knowledge, expertise, and organizational culture.
3. Success Criteria
Success is defined by specific objectives or outcomes that an organization aims to achieve. These criteria could include financial targets, market share goals, customer satisfaction levels, or other key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the organization’s mission and objectives.
4. Acceptable Levels of Risk
Risk tolerance varies depending on the organization’s risk appetite, strategic objectives, industry norms, and regulatory requirements. Identifying and quantifying acceptable levels of risk is essential for evaluating the feasibility of different scenarios and making informed decisions.
By delineating the FSS, organizations can navigate uncertainty and complexity, providing a structured framework for analyzing and evaluating alternative courses of action.
Establishing FSS involves quantitative analysis, qualitative judgment, scenario planning, and risk assessment techniques. Continuous monitoring and adaptation are also essential, as environmental conditions and organizational capabilities evolve over time.
Scenario Analysis: AI Race Between China and the United States
In exploring the dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, the race between China and the United States stands out as a pivotal contest with global implications. Both nations are investing heavily in AI, aiming to secure technological leadership, drive economic growth, and exert geopolitical influence. To understand the potential trajectories of this competition, the concept of Feasible Scenario Spaces (FSS) can be used. By applying FSS, it is possible to systematically analyze the various factors at play and envision different futures over the next decade. This approach not only highlights the strategic moves of these AI titans but also provides a framework for planning and navigating the uncertainties of the AI-driven world.
Research and Development (R&D) Investment:
Comparing the Research and Development (R&D) investment in Artificial Intelligence (AI) between the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the United States involves analyzing various factors such as funding allocation, government support, and private sector investment. Each aspect will be discussed and then graphed for comparison.
- Funding Allocation:
- CCP: The Chinese government has made significant investments in AI as part of its broader strategy to become a global leader in technology and innovation. This includes allocating funds to research institutions, universities, and companies engaged in AI development.
- US: The US government also invests heavily in AI research through agencies like the National Science Foundation (NSF), the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Additionally, private sector companies contribute substantially to AI research funding.
- Government Support:
- CCP: The Chinese government has outlined AI as a strategic priority in its national development plans, such as the “New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan.” This involves providing financial incentives, tax breaks, and regulatory support to AI companies and research institutions.
- US: The US government has shown bipartisan support for AI research and development, with initiatives like the American AI Initiative and the National Artificial Intelligence Research and Development Strategic Plan. Government support comes in the form of grants, contracts, and partnerships with academia and industry.
- Private Sector Investment:
- CCP: Chinese tech giants like Alibaba, Tencent, and Baidu are heavily investing in AI research and development, as are numerous startups in China’s vibrant tech ecosystem. The Chinese government’s policies, including venture capital support and access to markets, also facilitate private sector investment.
- US: Silicon Valley companies such as Google, Microsoft, Facebook, and Amazon are leading the way in AI research and development. Venture capital firms in the US provide significant funding to AI startups, driving innovation and competition in the market.
- Funding Sources: Allocation, Government, and Private Sector:
- Investment Amounts:
- CCP:
- Allocation: $50 billion
- Government: $30 billion
- Private Sector: $40 billion
- US:
- Allocation: $70 billion
- Government: $60 billion
- Private Sector: $80 billion
- CCP:
- Investment Amounts:
Talent Pool
The AI talent pool in both the United States and China is a critical factor in determining each country’s competitiveness and innovation prowess in artificial intelligence. Here’s a comparison of the AI talent pools between the two countries:
- United States:
- Historical Dominance: The US has been a global leader in AI research and development for decades, with prestigious universities like Stanford, MIT, and Carnegie Mellon at the forefront of AI innovation.
- Rich Ecosystem: Silicon Valley serves as a hub for tech giants, startups, research labs, and venture capital firms focused on AI. The presence of companies like Google, Microsoft, Facebook, and Amazon attracts top AI talent from around the world.
- Open Immigration Policies: The US has historically welcomed skilled immigrants, including researchers and engineers in AI-related fields, contributing to the diversity and talent pool in the country.
- Strong Academic Programs: US universities offer comprehensive AI programs and research opportunities, attracting both domestic and international students interested in pursuing careers in AI.
- China:
- Rapid Growth: China has made significant strides in AI research and development in recent years, supported by government initiatives, investment, and strategic planning.
- Growing Ecosystem: Tech hubs like Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen are home to a burgeoning AI ecosystem, including tech giants like Baidu, Alibaba, and Tencent, as well as numerous startups and research institutes.
- National Initiatives: The Chinese government has launched initiatives such as the “New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan” to foster talent development, attract overseas talent, and build a competitive AI industry.
- Investment in Education: China has been investing heavily in STEM education and research infrastructure, aiming to cultivate a new generation of AI talent domestically.
While both the US and China boast strong AI talent pools, there are some key differences:
- Focus Areas: The US has traditionally focused on fundamental research and cutting-edge AI technologies, while China has placed emphasis on applications of AI in areas like e-commerce, fintech, healthcare, and smart cities.
- Regulatory Environment: The regulatory environment in each country can influence the flow of talent. For example, US immigration policies and visa restrictions may impact the ability of foreign talent to work and study in the country.
- Cultural Factors: Cultural factors, including work culture, values, and incentives, may shape the preferences of AI talent regarding where to work and conduct research.
- Collaboration vs. Competition: While there is competition between the US and China in AI development, there are also opportunities for collaboration, knowledge exchange, and joint research projects that can benefit both countries and the global AI community.
Overall, the competition for AI talent between the US and China is intense, with each country leveraging its strengths and resources to attract and retain top talent in AI-related fields. The continued development of the AI talent pool will play a crucial role in shaping the future trajectory of AI innovation and applications in both countries and globally.
Technology Ecosystem
- United States:
- Universities and Research Institutions: The US is home to some of the world’s leading universities and research institutions in AI, such as MIT, Stanford, and Carnegie Mellon University. These institutions not only produce cutting-edge research but also train a significant portion of the global AI talent.
- Startups: The US has a vibrant startup ecosystem with numerous AI startups across various sectors including healthcare, finance, automotive, and more. Examples include OpenAI, Databricks, and Nuro. Silicon Valley remains a global hub for tech startups, providing a conducive environment for innovation, investment, and growth.
- Industry Giants: Major technology companies like Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Facebook are at the forefront of AI research and application. These companies invest heavily in AI and often acquire startups to bolster their capabilities. They contribute to both fundamental research and the commercialization of AI technologies.
- China:
- Universities and Research Institutions: Chinese universities like Tsinghua University, Peking University, and Zhejiang University have rapidly increased their focus on AI research and education. Research institutions such as the Chinese Academy of Sciences play a crucial role in AI research and innovation.
- Startups: China has seen a significant rise in AI startups, particularly in sectors like facial recognition, fintech, and autonomous vehicles. Examples include SenseTime, Megvii, and Pony.ai. Cities like Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen have become major tech hubs, fostering a thriving startup culture.
- Industry Giants: Leading Chinese tech companies such as Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent are heavily investing in AI. These companies have large AI research divisions and are involved in various AI applications from e-commerce to healthcare. Government-backed initiatives and funding also support these companies in scaling their AI capabilities.
Regulatory Environment
- United States:
- Government Policies: The US government has adopted a relatively laissez-faire approach to AI regulation, focusing on promoting innovation while addressing ethical and safety concerns. Key initiatives include the American AI Initiative, launched in 2019, which aims to prioritize AI research, increase access to AI resources, and promote international collaboration. The National AI Initiative Act of 2020 establishes a coordinated federal strategy for AI, emphasizing research and development, workforce training, and ethical AI deployment.
- Regulations: The regulatory environment in the US is characterized by sector-specific regulations rather than overarching federal AI regulations. This means different industries (e.g., healthcare, finance, transportation) are governed by relevant regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA, SEC, DOT). The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) oversees consumer protection and has issued guidelines on AI fairness, transparency, and accountability.
- Ethical Guidelines: The US has seen the development of various ethical frameworks and guidelines from both public and private sectors. Examples include the AI principles from the Department of Defense and ethical guidelines from companies like Google and Microsoft. Non-governmental organizations and academic institutions also contribute to the discourse on AI ethics, emphasizing issues like bias, fairness, and privacy.
- Challenges: The fragmented regulatory landscape can lead to inconsistencies and gaps in oversight. There is an ongoing debate about balancing innovation with regulation to ensure both economic growth and societal protection.
- China:
- Government Policies: The Chinese government has taken a proactive and centralized approach to AI regulation. The “New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan” (2017) outlines China’s strategic vision to become a global AI leader by 2030. The plan emphasizes AI development in areas such as smart cities, healthcare, and manufacturing, and encourages public-private partnerships.
- Regulations: China has implemented comprehensive regulations governing AI, often integrated with broader technology and cybersecurity laws. The Cybersecurity Law (2017) and the Data Security Law (2021) have significant implications for AI, particularly regarding data protection, privacy, and cross-border data flows. The Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL), which came into effect in 2021, is China’s primary data protection law, akin to the EU’s GDPR, and includes provisions relevant to AI systems.
- Ethical Guidelines: China has developed national ethical guidelines for AI, emphasizing principles like privacy protection, transparency, and social responsibility. The Beijing AI Principles and the AI ethics framework by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT) are key examples. The Chinese government promotes the use of AI for societal good and aligns ethical guidelines with its broader political and social objectives.
- Challenges: The centralized regulatory approach can lead to stringent controls that may stifle innovation. Balancing rapid AI development with ethical considerations remains a complex issue, particularly concerning surveillance and individual privacy.
Comparison and Implications
- Innovation vs. Regulation Balance:
- The US favors a more market-driven approach, promoting innovation with minimal regulatory interference, which can accelerate technological advancement but may lead to ethical and safety concerns.
- China’s centralized approach aims to steer AI development towards national goals, potentially ensuring ethical compliance but risking over-regulation.
- Data Privacy and Security:
- The US has a fragmented data privacy landscape with state-level laws (e.g., CCPA in California) and sector-specific regulations.
- China’s comprehensive data laws (e.g., PIPL) provide a unified framework for data protection, but strict controls could impact international collaboration and data flows.
- Ethical Considerations:
- Both countries emphasize AI ethics, but their approaches reflect broader political and social contexts. The US approach is more decentralized, with significant input from the private sector and academia.
- China’s approach is more top-down, aligning ethical guidelines with government policies and national priorities.
Understanding these regulatory environments is crucial for stakeholders, including multinational companies, policymakers, and researchers, to navigate the complex landscape of AI development and deployment in these two leading nations.
International Collaboration
- United States:
- Partnerships and Alliances: The US actively engages in international collaborations through partnerships with other leading AI nations, including the EU, Japan, Canada, and Israel. These collaborations often focus on joint research initiatives, standard-setting, and addressing global challenges. Organizations such as the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI), which includes the US, work to foster international cooperation in AI development and governance.
- Academic and Research Exchanges: US universities and research institutions frequently collaborate with international counterparts on AI projects. These collaborations involve joint research programs, academic exchanges, and co-publication of research papers. Funding agencies like the National Science Foundation (NSF) support international research partnerships through grants and collaborative projects.
- Industry Collaboration: US tech companies, including Google, Microsoft, IBM, and Amazon, have a global footprint and engage in international collaborations. These companies often establish research labs abroad, partner with foreign companies, and participate in global AI conferences and forums. Cross-border investments, mergers, and acquisitions are common as US companies seek to integrate global expertise and technologies.
- Government Initiatives: The US government promotes international collaboration through bilateral agreements, science and technology (S&T) cooperation agreements, and participation in global AI governance initiatives. The American AI Initiative encourages international collaboration to ensure the US remains a leader in AI while promoting ethical standards and addressing global challenges like climate change and health crises.
- China:
- Partnerships and Alliances: China has established AI partnerships with countries across Asia, Africa, Europe, and Latin America. These partnerships often involve technology transfer, joint research, and infrastructure development. Initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) include a focus on technology cooperation, with AI being a key component.
- Academic and Research Exchanges: Chinese universities and research institutions are increasingly collaborating with international counterparts. These collaborations include joint research projects, student and faculty exchanges, and participation in international conferences. Programs like the Thousand Talents Plan have aimed to attract top AI talent from around the world to China, fostering global knowledge exchange.
- Industry Collaboration: Chinese tech giants such as Alibaba, Baidu, Tencent, and Huawei engage in international collaborations, establishing research labs abroad, forming partnerships, and participating in global AI initiatives. China’s AI companies are active in global markets, contributing to AI applications and infrastructure development in various countries.
- Government Initiatives: The Chinese government promotes international collaboration through bilateral and multilateral agreements, focusing on AI research and development, standardization, and ethical governance. China is actively involved in international organizations and forums that shape AI policy and standards, such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the United Nations.
Comparison and Implications
- Approach to Collaboration:
- The US approach to international collaboration is often driven by both government and private sector initiatives, with a focus on maintaining leadership in AI while promoting ethical standards and addressing global challenges.
- China’s approach is more state-driven, aligning international collaborations with broader geopolitical and economic strategies, such as the BRI.
- Focus Areas:
- US collaborations often emphasize fundamental research, innovation, and ethical governance, leveraging its strong academic and private sector ecosystem.
- China’s collaborations emphasize technology transfer, infrastructure development, and practical AI applications, supporting its rapid industrialization and economic growth.
- Geopolitical Considerations:
- Geopolitical tensions between the US and China can impact the scope and nature of their international collaborations. For example, export controls, restrictions on technology transfer, and concerns about intellectual property theft can create barriers to collaboration.
- Both countries are seeking to build alliances and partnerships that can enhance their strategic positions in the global AI landscape.
- Ethical and Governance Issues:
- The US promotes international collaboration on AI ethics and governance, emphasizing democratic values, human rights, and transparency.
- China is also involved in shaping global AI governance but tends to align these efforts with its national priorities and regulatory frameworks, which can differ significantly from Western norms.
Understanding the dynamics of international collaboration in AI is crucial for stakeholders navigating the complex interplay of innovation, competition, and cooperation in the global AI landscape. Both the US and China play pivotal roles in shaping the future of AI through their international partnerships and alliances.
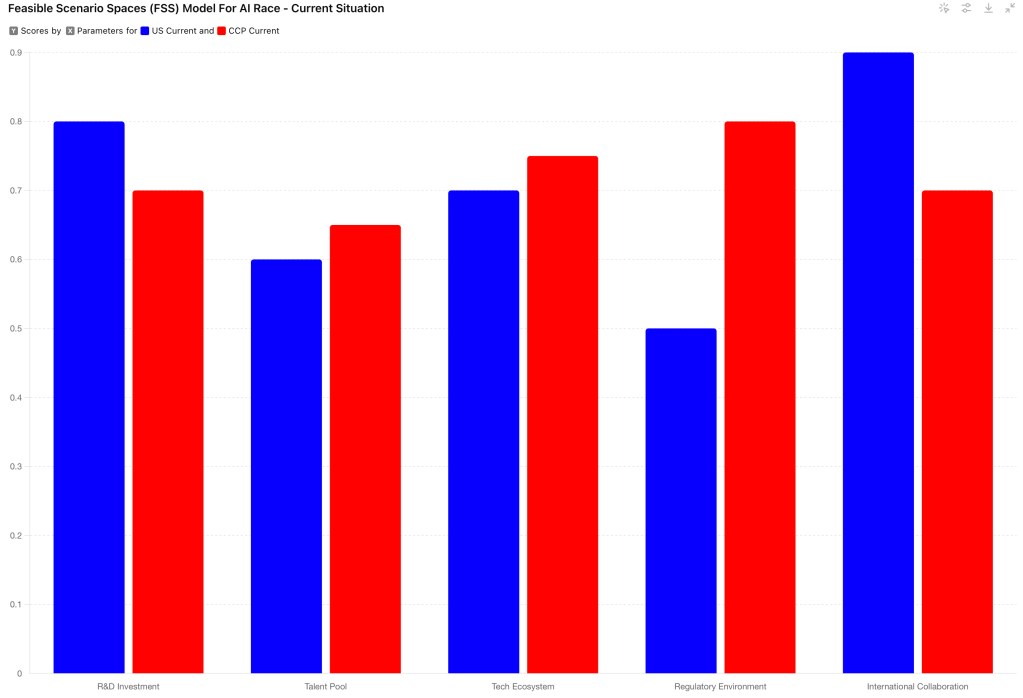
Data Sources and Explanation for Talent Pool and Tech Ecosystem
Talent Pool
US:
- Current Score: 0.6
- The US has historically been a leader in AI research and development, with top universities like MIT, Stanford, and Carnegie Mellon.
- The US benefits from a rich ecosystem in Silicon Valley, attracting global talent.
- However, recent challenges include stricter immigration policies and increased competition for global AI talent.
CCP:
- Current Score: 0.65
- China has rapidly expanded its AI talent pool through substantial investment in education and research.
- Government programs like the Thousand Talents Plan aim to attract global experts to China.
- The emphasis on STEM education and substantial funding for AI research have boosted the talent pool.
Tech Ecosystem
US:
- Current Score: 0.7
- The US boasts a highly innovative tech ecosystem with leading companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon driving AI advancements.
- Silicon Valley serves as a global hub for tech startups and innovation.
- The collaboration between academia and industry strengthens the tech ecosystem.
CCP:
- Current Score: 0.75
- China has made significant strides in building a robust tech ecosystem with giants like Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent.
- The Chinese government supports tech innovation through funding and favorable policies.
- China’s focus on practical AI applications in areas like e-commerce, fintech, and smart cities has led to rapid growth.
Explanation for CCP Lead in Talent Pool and Tech Ecosystem
Talent Pool:
- Expansion Efforts: China’s government has actively worked to grow its domestic talent pool through initiatives and substantial investments in education and research. Programs like the Thousand Talents Plan have successfully attracted global experts to China.
- Focus on STEM: China places a strong emphasis on STEM education, ensuring a steady supply of new graduates in AI-related fields.
- Government Support: Continuous government backing and funding for AI research and development help to maintain and grow the talent pool.
Tech Ecosystem:
- Government Policies: The Chinese government provides significant support to the tech industry, including financial incentives, regulatory support, and infrastructure development.
- Major Tech Companies: Leading tech firms in China like Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent are heavily investing in AI and driving innovation.
- Rapid Growth: The practical application of AI in various sectors such as e-commerce, fintech, healthcare, and smart cities has accelerated the development of China’s tech ecosystem.
- Strategic Planning: China’s strategic plans, such as the “New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan,” emphasize the importance of AI and provide a clear roadmap for technological advancement.
10-Year Projection
Looking into the future, the competition between the United States and China in the realm of artificial intelligence intensifies. Although a crystal ball is lacking, the concept of Feasible Scenario Spaces (FSS) can be leveraged to anticipate potential trends and developments over the next decade. FSS allows strategists to explore how these AI titans might shape the technological, economic, and geopolitical landscape in 2034. By examining key parameters, capabilities, and success criteria, strategic pathways can be outlined and plans made for an AI-driven future.
- Technological Advancements:
- China: Significant strides in AI applications and hardware development, making China a dominant force in practical AI solutions.
- US: Continues to lead in innovation and foundational AI research, setting global benchmarks and standards.
- Economic Growth:
- China: Rapid economic growth driven by AI deployment, with an expanding influence in global markets.
- US: Sustains economic growth through AI-driven innovations and a competitive tech ecosystem.
- Global Influence:
- China: Promotes its AI governance models and standards through international collaborations and strategic initiatives.
- US: Remains influential in shaping international AI standards and governance, fostering a collaborative global AI ecosystem.
- Ethical Leadership:
- China: Implements robust regulatory measures to ensure responsible AI deployment, focusing on social stability and national security.
- US: Continues to emphasize ethical AI frameworks and transparency, influencing global practices and norms.
- Security and Stability:
- China: Focuses on secure and resilient AI systems, supported by government regulations and investments.
- US: Develops advanced cybersecurity measures and resilient AI technologies, ensuring safe AI innovation.

Explanation for the US Passing the CCP in Talent Pool and Tech Ecosystem by 2035
Talent Pool
Current Situation:
- US: The US currently has a strong AI talent pool driven by its world-class universities, vibrant tech industry, and a long history of leading in AI research. However, challenges such as restrictive immigration policies and intense global competition for talent have hindered its growth.
- CCP: China has rapidly expanded its AI talent pool through significant investments in education and initiatives like the Thousand Talents Plan, attracting global experts and focusing on STEM education.
Future Projections for 2035:
- US:
- Policy Reforms: Anticipated reforms in immigration policies will attract more global talent to the US. Policies encouraging STEM education and research will bolster the domestic talent pool.
- Educational Initiatives: Increased investment in AI-specific educational programs at top universities and the establishment of new AI research institutes will enhance the talent pipeline.
- Industry-Academia Collaboration: Strengthened partnerships between industry and academia will facilitate the practical application of AI research and provide more opportunities for students and researchers.
- CCP:
- Sustained Growth: While China will continue to grow its talent pool, the US will capitalize on its existing strengths and new initiatives to surpass China.
- Potential Constraints: Issues such as political constraints, censorship, and a less open academic environment might limit the free exchange of ideas, which is crucial for innovation.
Tech Ecosystem
Current Situation:
- US: The US has a highly innovative tech ecosystem with leading companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon. Silicon Valley remains a global hub for tech startups and innovation.
- CCP: China has developed a robust tech ecosystem with major firms like Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent, supported by significant government investment and a focus on practical AI applications.
Future Projections for 2035:
- US:
- Innovation Leadership: Continued leadership in foundational AI research and development will drive advancements in the tech ecosystem. Companies like Google and OpenAI are expected to make significant breakthroughs.
- Startup Ecosystem: A vibrant startup ecosystem supported by venture capital and strong industry-academia ties will foster innovation and commercialization of new AI technologies.
- Policy Support: Government policies supporting innovation, ethical AI, and public-private partnerships will further strengthen the tech ecosystem.
- CCP:
- Sustained Development: China’s tech ecosystem will continue to grow, but the US will leverage its existing strengths and new strategic initiatives to outpace China.
- Regulatory Challenges: Stringent regulations and political controls might stifle some aspects of innovation, limiting the potential growth of the tech ecosystem.
By implementing strategic reforms and capitalizing on its existing strengths, the US is projected to surpass the CCP in both the Talent Pool and Tech Ecosystem by 2035. This advancement is driven by policy reforms, educational initiatives, industry-academia collaboration, innovation leadership, a robust startup ecosystem, and supportive government policies.
Conclusion
The AI race between China and the United States will continue to shape the global landscape over the next decade. Each country leverages its unique strengths and strategic approaches to drive technological advancements, economic growth, and global influence. While the US maintains its leadership in innovation and ethical frameworks, China rapidly advances in practical AI applications and global markets. The interplay between these two AI powerhouses will drive significant technological progress, shaping the future of AI globally. Continuous monitoring, adaptation, and international collaboration will be crucial for managing risks and maximizing opportunities in this dynamic and uncertain environment.



